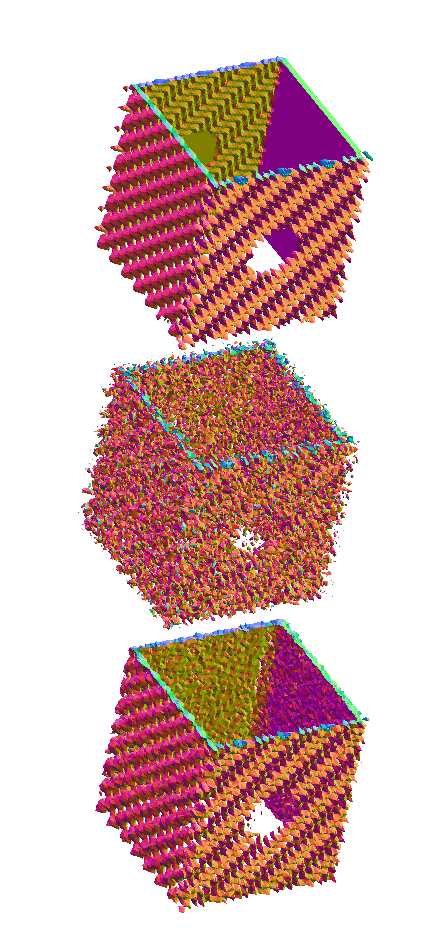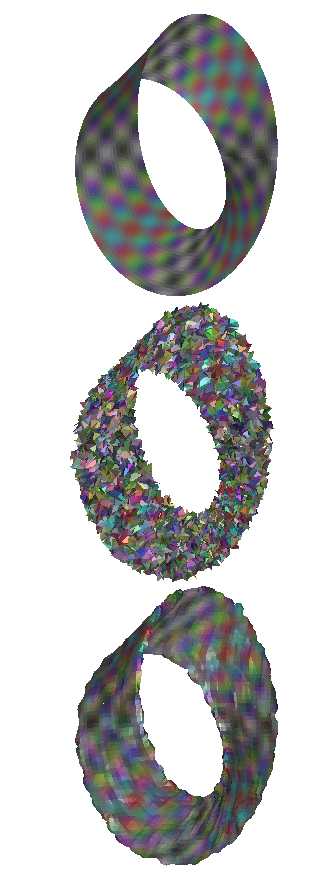GASDYNAMICS
In this study, we investigate how can we
concentrate energy in a point by focusing shock waves. One open problem
is what happens when the shock waves are not circularly symmetric. Here
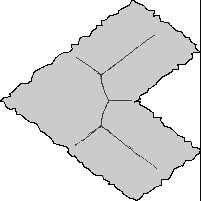
we show a numerical simulation of a non-circular
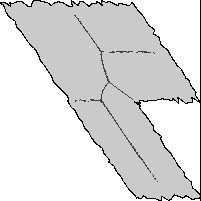
convergent shock wave on a gas with gamma=1.4. The second picture
shows an advanced stage of the focusing at a scale 8 times smaller
than the first picture. We found that under the right conditions, the
shock waves form a triangular pattern that is stable.

POROUS MEDIUM EQUATION
Here we do a similar study, but instead
of shock waves in a gas, we have a flow of gas into a porous medium. We
found that there is a family of selfsimilar solutions describing the
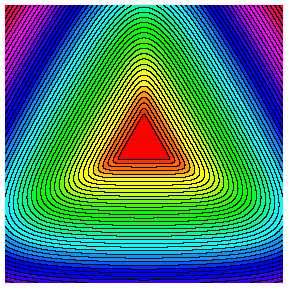
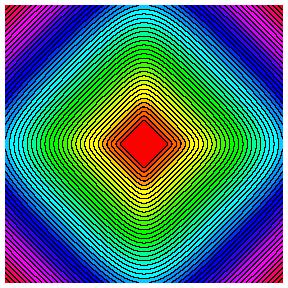
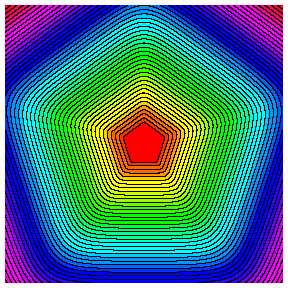
focusing. Contour lines of the selfsimilar solutions of the second
kind:
convergent currents in two dimensions. From left to right: 3-fold
symmetry and m=1.3, 4-fold symmetry and m=1.2, 5-fold
symmetry and m=1.1.
Focusing solution for an elongated hole:
non-selfsimilar solution.
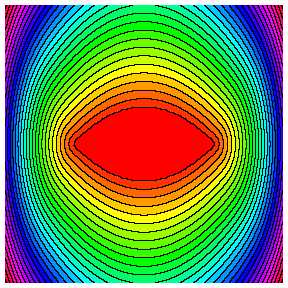
Zipper solutions describe 2D
singularities on
the solutions of the porous medium equation. They are selfsimilar
travelling waves. Similar solutions also exist for flows driven by
capillarity. These solutions are useful counterexamples of the
regularity of the interfaces in special cases (here the interface is a
half line).
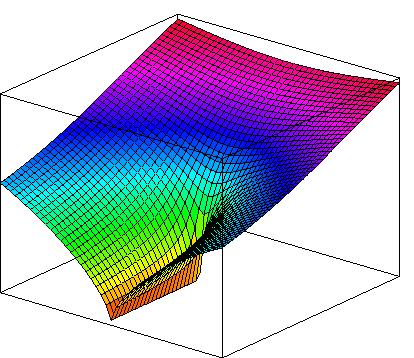
VERY VISCOUS FLOWS
Spreading of a blob of viscous fluid on a flat surface: boundary
elements method simulation for the Stokes flow. The insert shows the
streamlines near the 'nose' of the viscous current.
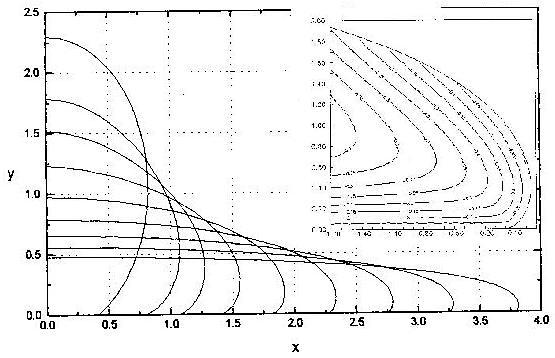
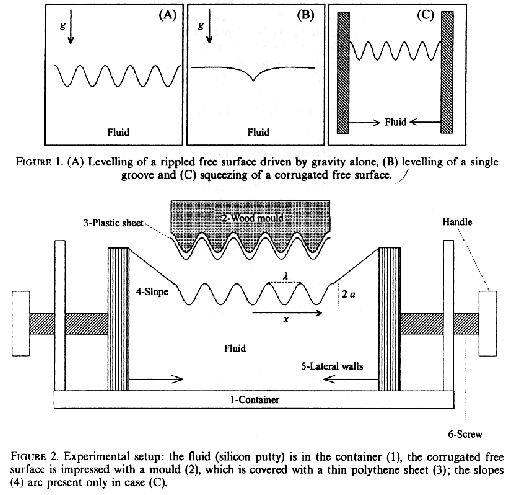
My experiment on the
corrugation of very viscous fluids
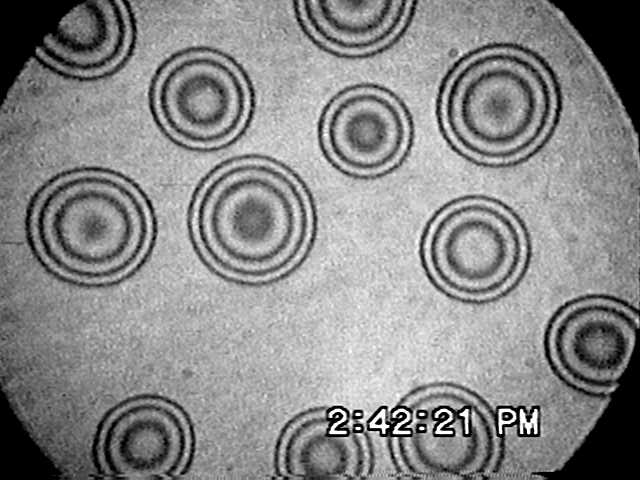
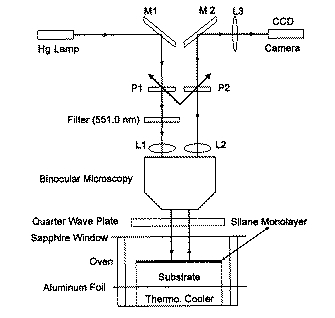
STUDIES ON WETTING TRANSITION
Micro-interferogram of droplets of nonane near the wetting
transition on a C8 Silane monolayer, at a temperature of 33.1C.
Sketch of the microscope that I designed and built
with Jiang and Bruce for obtaining the previous picture
SMOOTHING OF TEXTURED 2D IMAGES
Here we explore a powerful method to
denoise color images. Synthetic picture showing texture in color. The
image is
corrupted in order to destroy the texture and then the image is
partially restored with a pseudo-local filter.
SOURCE
CODE.


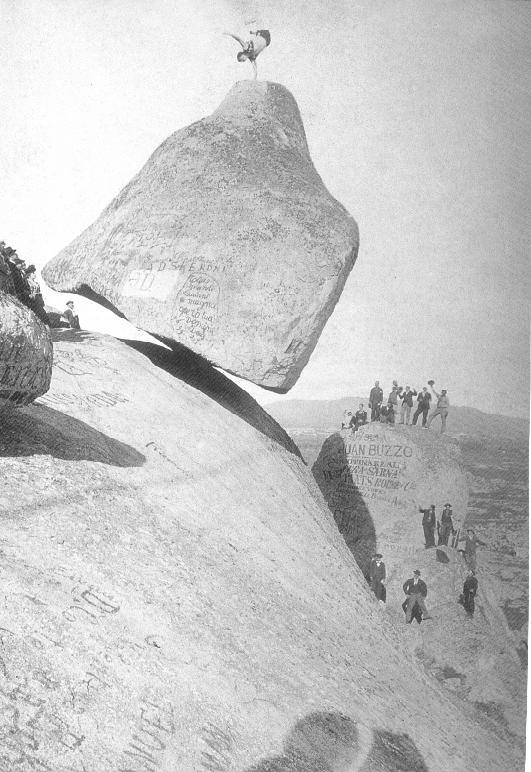
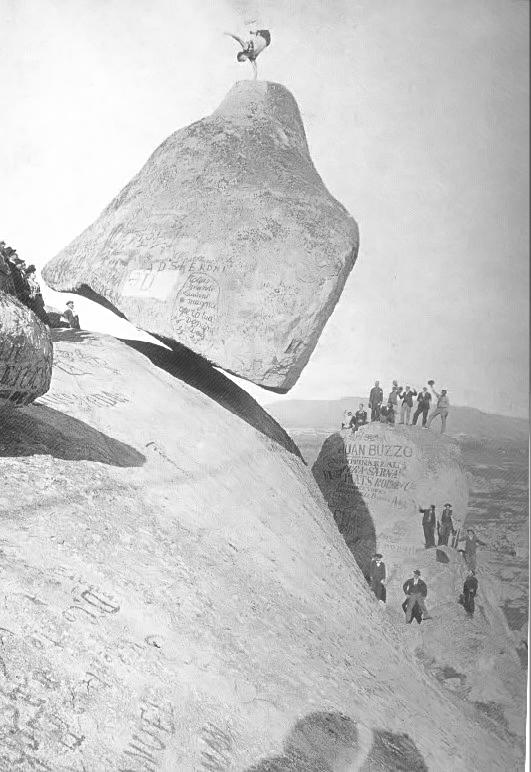
Photograph (Piedra Movediza Del Tandil) restored with
the pseudo-local filter. The original noisy image is on the left and
it is restored on the right preserving the texture of the stone.
Processing time: 3.5 sec in a PC-600 Mhz.


SMOOTHING
OF TEXTURED 3D DATA
Synthetic 64x64x64 tomography of a
hollow cube with texture (top). The color RGB components are
proportional to the three components of the local unit normal of the
surface. The data is corrupted with noise in order to ruin the
texture (center). The image is restored with a pseudo-local filter
(bottom).
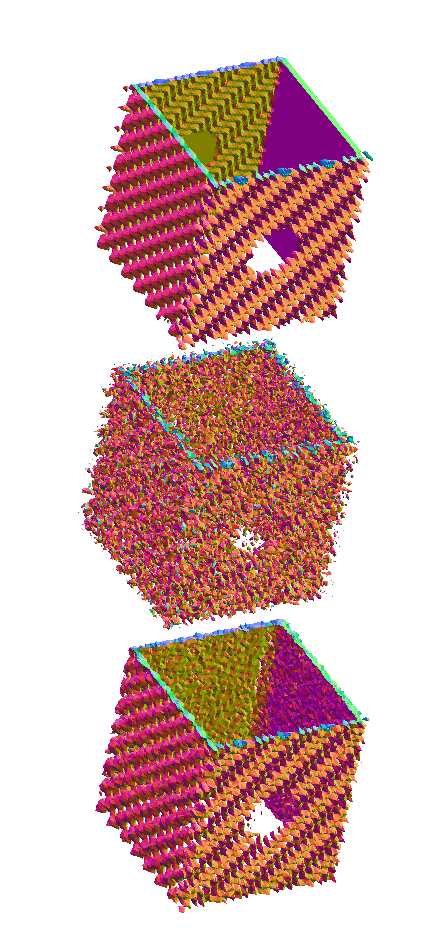
Triangulated Moebius srip with a color pattern (top).
Noise is added to both the color pattern and the shape
(center). The shape is partially restored with a combination PDE's
and a pseudo-local filter (bottom).
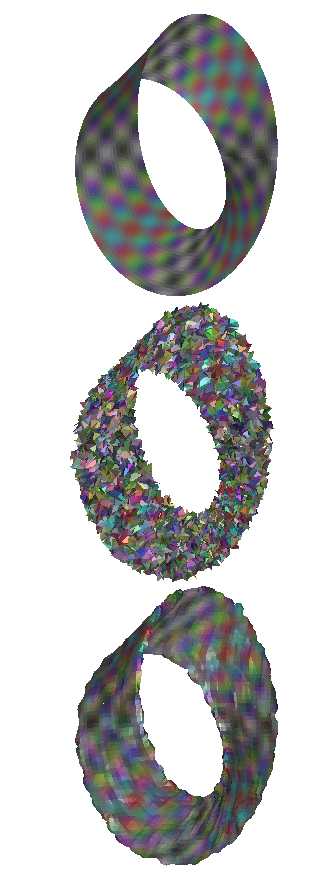
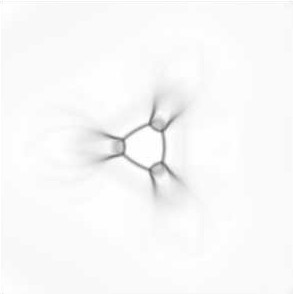
SKELETONS
Affine
invariant skeleton (inner points) of a shape with noise (outer curve,
left). The same figure was skewed out, in order to show the affine
invariance of the skeleton (right). Straight lines in the skeleton
may be associated with skew-symmetry.
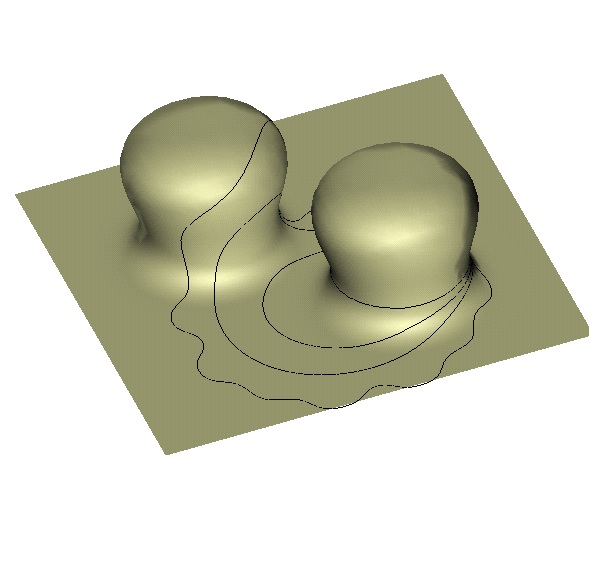
GEODESIC CURVATURE FLOW
Evolution of a curve on a surface. The velocity of the curve is
equal to the geodesic curvature. The curve converges to a geodesic in
this example.